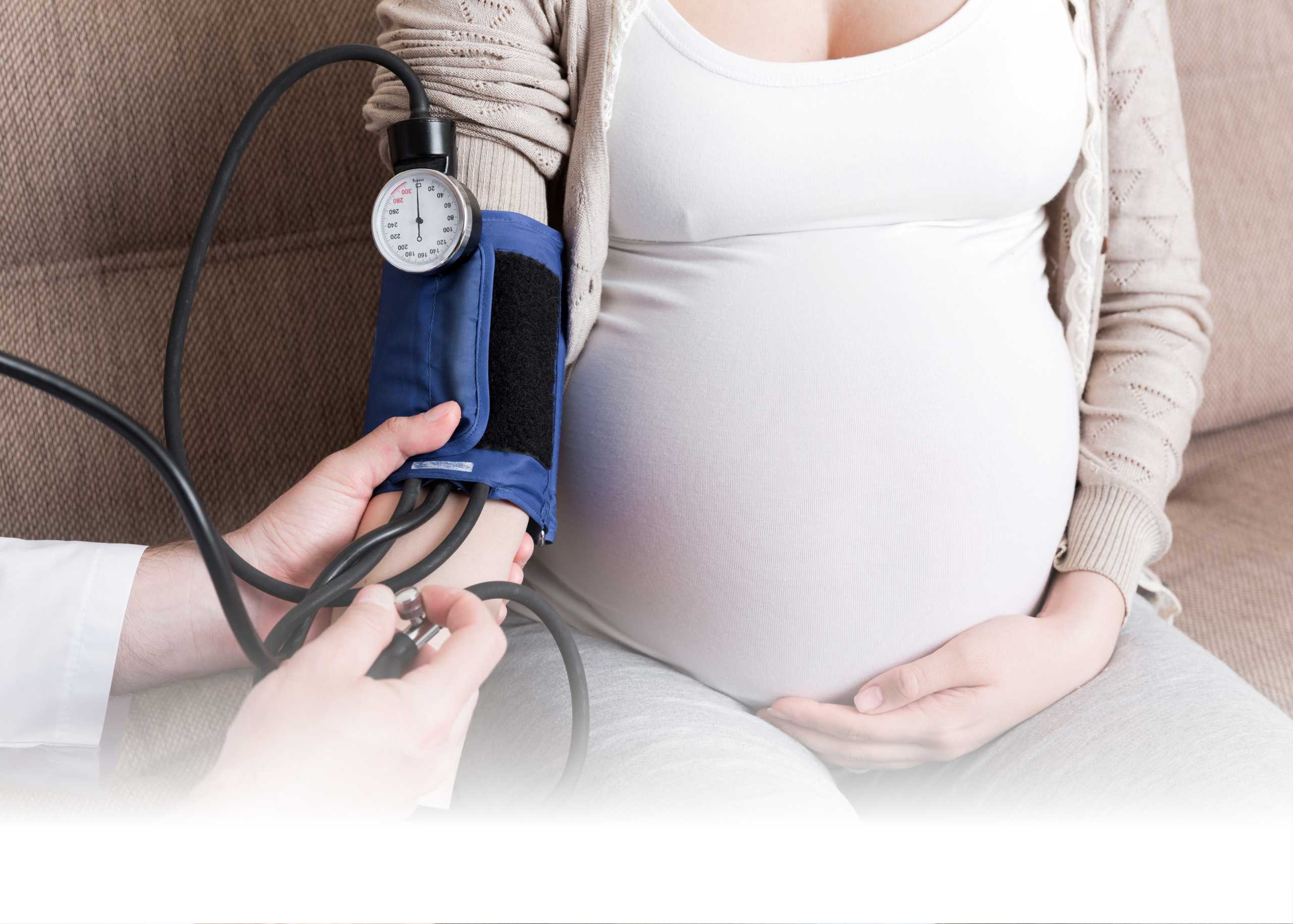
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is crucial at every stage of life, but during pregnancy, it becomes even more important—for both the mother’s and the baby’s well-being. At Medeor Hospital, Abu Dhabi, we prioritize maternal health with comprehensive prenatal care that includes blood pressure monitoring and management.
In this blog, we’ll explore everything you need to know about blood pressure during pregnancy—from what’s considered normal to warning signs you should never ignore.
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. It’s measured using two numbers:
- Systolic pressure (top number): Pressure when your heart beats.
- Diastolic pressure (bottom number): Pressure when your heart rests between beats.
For most adults, a normal blood pressure is around 120/80 mmHg. During pregnancy, these numbers can change due to hormonal shifts and the body’s increased blood volume.
Types of Blood Pressure Issues in Pregnancy
There are several types of blood pressure conditions that may occur during pregnancy:
1. Chronic Hypertension
- High blood pressure diagnosed before pregnancy or before 20 weeks of gestation.
- May continue after delivery.
- Requires careful monitoring and possible medication adjustment.
2. Gestational Hypertension
- High blood pressure that develops after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Usually temporary and resolves after childbirth.
- Can lead to more serious conditions if untreated.
3. Preeclampsia
- A serious condition that includes high blood pressure and organ damage, typically affecting the liver and kidneys.
- Symptoms include protein in urine, swelling, vision changes, and headaches.
- Can be dangerous for both mother and baby, requiring immediate medical attention.
4. Eclampsia
- A severe complication of preeclampsia that involves seizures.
- Considered a medical emergency.
Normal Blood Pressure Range During Pregnancy
- Ideal range: 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg
- Slight fluctuations are normal due to hormonal and physiological changes.
- Persistent readings above 140/90 mmHg may indicate hypertension.
Symptoms of Blood Pressure to Watch For
While high blood pressure during pregnancy may not always cause obvious symptoms, some warning signs include:
- Severe headaches
- Blurred vision or light sensitivity
- Swelling in hands, feet, or face
- Sudden weight gain
- Upper abdominal pain
- Decreased urine output
- Shortness of breath
If you experience any of these, seek immediate care at a trusted hospital like Medeor Hospital, Abu Dhabi.
How Blood Pressure Affects Pregnancy
Uncontrolled blood pressure during pregnancy can lead to complications such as:
- Low birth weight
- Preterm birth
- Placental abruption
- Growth restriction
- Stillbirth (in severe cases)
That’s why early detection and consistent monitoring are essential.
How to Manage Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Here are some effective ways to manage and maintain healthy blood pressure:
Regular Prenatal Visits
Routine check-ups help detect issues early. Our obstetricians at Medeor Hospital monitor your blood pressure and overall health throughout your pregnancy.
Healthy Diet
Eat a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Limit salt, caffeine, and processed foods.
Stay Active
Engage in safe pregnancy-friendly exercises like walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga (after consulting your doctor).
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps regulate blood volume and prevent dehydration-related spikes in blood pressure.
Medication (if prescribed)
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may prescribe pregnancy-safe medications to manage hypertension.
Reduce Stress
Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, breathing exercises, or prenatal massage.
Why Choose Medeor Hospital, Abu Dhabi?
At Medeor Hospital, we offer:
- Experienced gynecologists and obstetricians
- Advanced maternal-fetal medicine services
- 24/7 emergency care for pregnancy complications
- Personalized prenatal monitoring plans
- A compassionate, patient-first approach to maternity care
Our goal is to ensure a safe, healthy pregnancy journey for you and your baby.
Final Thoughts
Monitoring blood pressure during pregnancy is not just a medical formality—it’s a vital part of ensuring the best possible outcome for both mother and child. With the right care, education, and expert support from Medeor Hospital, Abu Dhabi, you can confidently navigate your pregnancy knowing you are in safe hands. If you’re expecting or planning to conceive, book a prenatal consultation with our experts today and take the first step toward a healthy pregnancy.