Ramadan is a time of reflection, discipline, and spiritual renewal. Alongside its spiritual significance, fasting during Ramadan also brings changes to daily routines, eating patterns, sleep cycles, and energy levels. When approached mindfully, fasting can support both physical health and mental wellbeing. However, without proper care, it may also lead to fatigue, dehydration, or mood changes.
This guide shares practical, doctor-recommended tips to help you fast safely and stay healthy throughout Ramadan.
Understanding Fasting and the Body
During Ramadan, the body shifts from regular meal timings to extended periods without food or water. This change affects blood sugar levels, hydration status, digestion, sleep, and concentration. With balanced nutrition, adequate rest, and mindful habits, most healthy adults can fast safely.
People with chronic medical conditions should always consult a doctor before fasting.
Practical Tips for Physical Wellbeing During Ramadan
1. Never Skip Suhoor
Suhoor is essential for maintaining energy during fasting hours. Skipping it increases the risk of fatigue, headaches, and low blood sugar.
Choose foods that release energy slowly, such as:
- Whole grains (oats, brown bread)
- Eggs, yogurt, or lean protein
- Fruits and vegetables
- Healthy fats like nuts or olive oil
Avoid salty and heavily fried foods, as they increase thirst during the day.
2. Hydrate Smartly Between Iftar and Suhoor
Dehydration is one of the most common Ramadan health concerns.
Tips for better hydration:
- Drink water steadily between Iftar and Suhoor, focusing on 8-10 glasses.
- Limit caffeinated drinks, as they increase fluid loss
- Include water-rich foods like fruits, soups, and salads
Aim for consistent hydration rather than large amounts at once.
3. Break the Fast Gently
Iftar should replenish energy without overwhelming the digestive system.
A healthy Iftar approach:
- Start with dates and water
- Follow with soup or light starters
- Choose balanced meals with protein, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates.
- Junk foods, fried foods, fast foods, sugary drinks to be avoided after break the fasting.
Avoid overeating and excessive fried or sugary foods, which can cause bloating, lethargy, and weight gain.
4. Maintain Light Physical Activity
While intense workouts may not be suitable during fasting hours, gentle movement supports circulation and mental clarity.
Good options include:
- Light stretching
- Walking after Iftar
- Gentle yoga or mobility exercises
Listen to your body and avoid strenuous activity during peak fasting hours.
Supporting Mental Wellbeing During Ramadan
5. Protect Your Sleep Routine
Late-night prayers and early Suhoor can disrupt sleep, affecting mood and focus.
Sleep tips:
- Aim for short daytime naps if needed
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Limit screen time before bed
Adequate rest improves emotional balance and concentration.
6. Manage Stress and Energy Levels
Fasting can increase irritability or mental fatigue, especially in the first week.
Helpful strategies include:
- Mindful breathing and reflection
- Planning tasks earlier in the day
- Reducing unnecessary commitments
- Allowing mental rest between prayers and work
Ramadan is also about slowing down—mentally and emotionally.
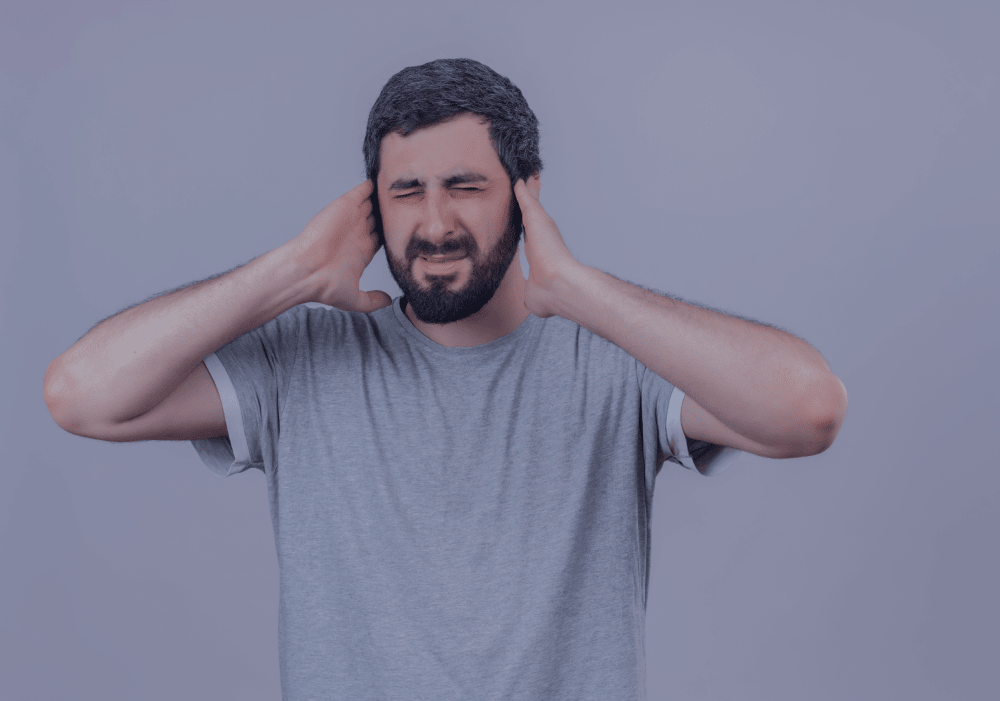
7. Know When to Seek Medical Advice
You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent dizziness or weakness
- Severe headaches
- Fainting or confusion
- Uncontrolled blood sugar levels
- Dehydration symptoms
People with diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, gastrointestinal conditions, or those who are pregnant should seek medical advice before fasting.
Who Should Take Extra Care While Fasting?
While many people can fast safely, extra medical guidance is recommended for:
- Individuals with diabetes or heart conditions
- Elderly individuals
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- People taking regular medications
- Individuals with kidney or gastrointestinal disorders
A pre-Ramadan health check can help ensure a safe fasting experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is fasting during Ramadan healthy?
For most healthy adults, fasting can be safe and beneficial when done with proper nutrition and hydration.
2. Can people with medical conditions fast?
Some can, with medical supervision. Always consult a doctor before fasting if you have a chronic condition.
3. What is the best food to eat at Suhoor?
Foods rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats help maintain energy and reduce hunger.
4. How can I avoid dehydration during Ramadan?
Drink water regularly between Iftar and Suhoor and limit caffeine and salty foods.
5. Is it okay to exercise while fasting?
Yes, light exercise is safe for most people, preferably after Iftar or close to it.
6. When should I stop fasting and seek medical help?
If you experience severe weakness, confusion, fainting, or signs of dehydration, stop fasting and seek medical care immediately.
Conclusion
Healthy fasting during Ramadan is about balance—between nourishment and restraint, rest and activity, body and mind. With thoughtful food choices, proper hydration, mindful routines, and medical guidance when needed, fasting can support both physical health and mental wellbeing. Listening to your body and seeking expert advice ensures Ramadan remains a time of peace, strength, and renewal.
Ramadan Health Support at Medeor Hospital, Abu Dhabi
If you’re planning to fast during Ramadan and want to ensure it’s safe for your health, Medeor Hospital, Abu Dhabi offers expert medical consultations, preventive health checks, and personalized guidance.
Book your consultation today and fast with confidence and peace of mind.