Introduction: The Silent Struggle of Men’s Mental Health
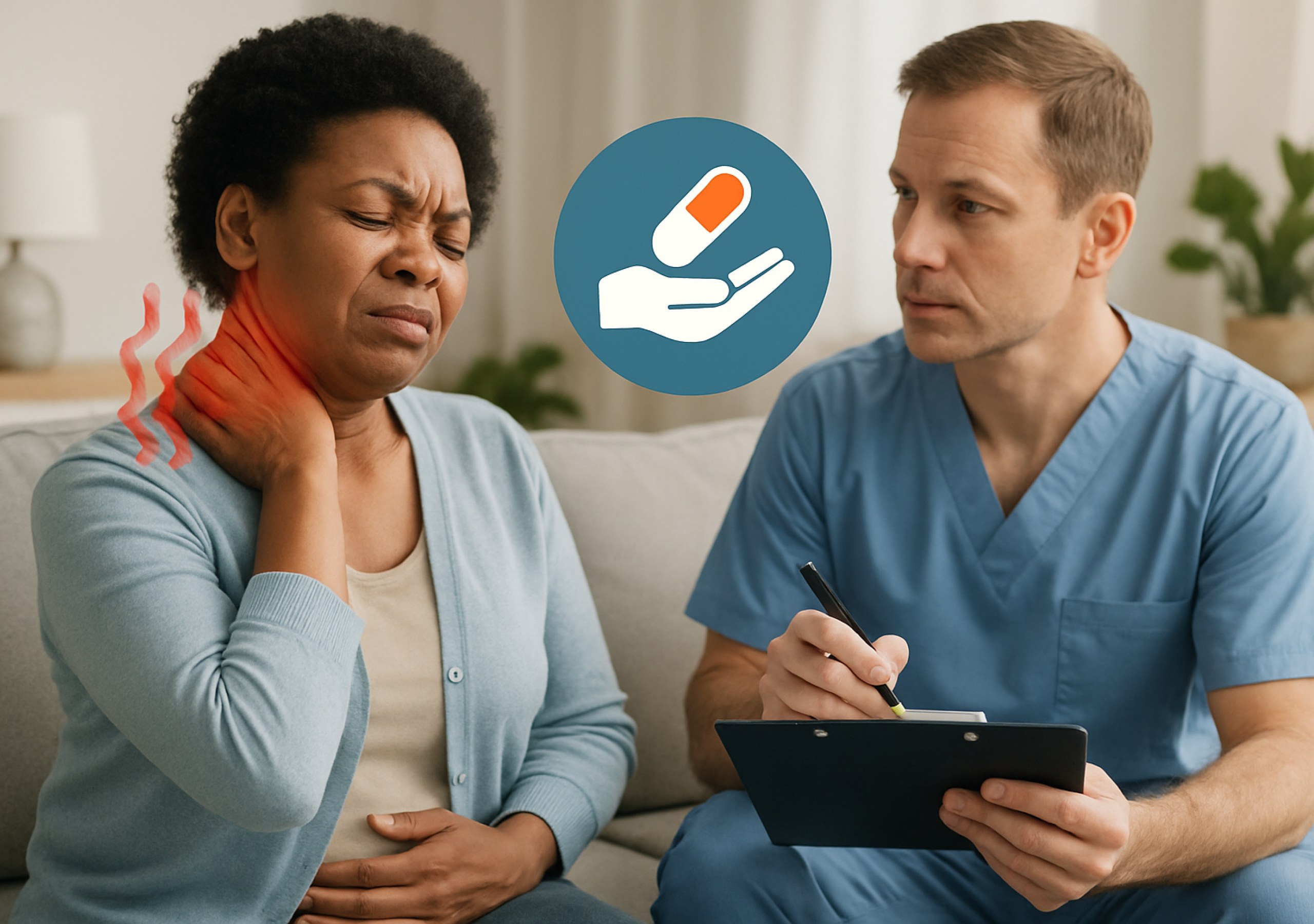
For generations, men have been taught to “stay strong,” “tough it out,” and “keep emotions in check.” But behind that mask of resilience, countless men silently battle stress, anxiety, and depression.
Men’s mental health is often overlooked—not because it’s less important, but because it’s less discussed. The truth is, silence doesn’t make pain disappear; it only deepens it.
At Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi, we believe it’s time to change the conversation. Mental health isn’t a weakness—it’s a vital part of men’s emotional wellness, and seeking help is a sign of courage, not failure.
The Reality: Depression in Men Is Often Invisible
Depression in men looks different than it does in women. While women may express sadness openly, men often internalize their feelings—turning them into anger, irritability, or withdrawal.
Many men dismiss their symptoms as “just stress” or “being tired.” But depression can affect every aspect of life—career, relationships, sleep, and physical health.
Common Signs of Depression in Men
- Persistent sadness or emptiness
- Irritability or anger outbursts
- Lack of interest in hobbies or intimacy
- Fatigue or difficulty sleeping
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Feelings of hopelessness or guilt
- Increased reliance on alcohol or nicotine
Recognizing these symptoms early is the first step toward healing. Depression isn’t a personal flaw—it’s a medical condition that deserves treatment and understanding.
Anxiety in Men: The Hidden Companion
Anxiety is one of the most common yet misunderstood mental health issues among men. It’s not just “worrying too much”—it’s a constant, uncontrollable tension that affects both body and mind.
Signs You Might Need Anxiety Treatment for Men
- Racing thoughts that won’t stop
- Restlessness, agitation, or muscle tension
- Difficulty concentrating
- Rapid heartbeat, sweating, or dizziness
- Trouble sleeping due to overthinking
At Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi, our experts provide holistic anxiety treatment for men, combining therapy, relaxation techniques, and—when needed—medication to help men regain calm, focus, and confidence.
The Pressure to Be ‘Strong’: Why Men Avoid Help
Society often defines masculinity through strength, success, and control. As a result, many men suppress emotions rather than express them—believing that seeking mental health support is a sign of weakness.
This stigma is one of the biggest barriers to men’s counseling services and therapy. But the truth is, asking for help is not a defeat—it’s a decision to take control of your life again.
Mental health challenges don’t discriminate. CEOs, athletes, fathers, and teenagers alike can all experience them. The real strength lies in recognizing the issue and reaching out for help.
Therapy for Men: Breaking the Taboo
Therapy for men is not about being told what to do—it’s about being heard, understood, and guided toward healthier ways of coping.
At Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi, we offer a safe, confidential environment where men can explore their thoughts and emotions with licensed experts—including a male psychologist in Abu Dhabi for those who feel more comfortable opening up to another man.
What Therapy Can Help With
- Depression, anxiety, and mood swings
- Relationship or marital issues
- Anger management and emotional regulation
- Stress management for men
- Work burnout and performance pressure
- Trauma or loss
Therapy helps men build resilience, not dependence. It provides tools for better decision-making, self-awareness, and emotional growth.
Stress Management for Men: Finding Balance in a Fast-Paced World
Today’s men are under constant pressure to provide, perform, and succeed. But that nonstop hustle often leads to chronic stress—a major risk factor for both mental and physical illnesses.
Simple Stress Management Techniques
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity releases endorphins that improve mood.
- Sleep well: Aim for 7–8 hours to recharge both mind and body.
- Practice mindfulness: Meditation or deep breathing helps clear mental clutter.
- Set boundaries: Learn to say no and manage time effectively.
- Talk about it: Share how you feel with a trusted friend, therapist, or support group.
Effective stress management for men isn’t about avoiding pressure—it’s about learning how to navigate it without breaking down.
Men’s Emotional Wellness: Redefining Strength
Men’s emotional wellness is not the absence of struggle—it’s the ability to handle emotions constructively. Society is beginning to redefine what “strength” means, emphasizing empathy, vulnerability, and connection.
Emotionally well men don’t bottle up emotions—they process them, communicate clearly, and seek support when needed. This mindset creates stronger relationships, better work performance, and improved physical health.
How Mental Health Affects Physical Health
Poor mental health can trigger physical issues such as high blood pressure, insomnia, or digestive problems. Chronic stress and depression in men can even increase the risk of heart disease and weakened immunity.
Conversely, improving mental health has measurable physical benefits: better energy, sleep, and immunity. It’s a reminder that men’s mental health and physical wellness are deeply intertwined.
Men’s Counseling Services at Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi
At Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi, our men’s counseling services are designed with men’s specific needs in mind—offering professional guidance in a confidential, understanding environment.
Our Approach Includes:
- Personalized therapy: One-on-one sessions with experienced psychologists.
- Group counseling: Safe spaces to share experiences and reduce stigma.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Evidence-based methods to reframe negative thoughts.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Tools for managing anxiety and improving focus.
- Holistic care: Collaboration between psychologists, nutritionists, and fitness experts to enhance overall men’s wellness.
Whether you’re facing burnout, emotional fatigue, or uncertainty, we’re here to help you rebuild your balance and confidence.
Men’s Mental Health Awareness: Changing the Narrative
It’s time to normalize the conversation. Men’s mental health awareness campaigns worldwide are urging men to speak openly about how they feel. When men talk, stigma breaks—and healing begins.
Encouraging workplaces, families, and communities to support men in seeking help can transform lives. Mental health isn’t just personal—it’s collective. The more we talk about it, the more lives we save.
FAQs on Men’s Mental Health
1. Why is men’s mental health often ignored?
Because of societal expectations that men should be “tough,” many avoid expressing vulnerability or seeking help.
2. What are the early signs of depression in men?
Irritability, anger, sleep issues, loss of motivation, and emotional withdrawal are common early signs.
3. How can therapy help men?
Therapy for men helps identify emotional triggers, improve coping mechanisms, and strengthen mental and emotional resilience.
4. Where can I find professional help in Abu Dhabi?
Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi offers men’s counseling services and access to a qualified male psychologist in Abu Dhabi for personalized care.
5. What’s the best way to manage stress?
Combine stress management for men techniques such as exercise, meditation, and therapy for long-term stability.
6. Can anxiety be treated without medication?
Yes. Many men benefit from anxiety treatment for men using therapy, mindfulness, and lifestyle changes—though medication may help in severe cases.
7. How can I support a friend struggling with mental health?
Listen without judgment, encourage professional help, and stay connected. Sometimes, being there is enough.
8. Why is emotional wellness important for men?
Men’s emotional wellness enhances self-esteem, relationships, and physical health—helping men lead balanced, fulfilling lives.
Q9. Are counseling services confidential?
Yes. All men’s counseling services at Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi are 100% confidential and conducted in a safe, private environment.
Q10. What is men’s mental health awareness about?
It’s about promoting open discussion, breaking stigma, and ensuring that men know it’s okay to ask for help.
Conclusion: It’s Okay to Talk, It’s Brave to Heal
Talking about men’s mental health doesn’t make you weak—it makes you wise. Bottling up emotions is not strength; it’s silence that hurts. Real resilience begins when men choose to heal instead of hide.
At Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi, our psychologists and counselors specialize in providing compassionate, confidential care tailored to men’s needs. Whether you’re dealing with depression in men, anxiety, or burnout, help is always available—and recovery is always possible.
Because the bravest thing you can do isn’t to suffer in silence—it’s to start the conversation.
Take the first step toward better mental health today.
Book your confidential consultation with our expert psychologist or explore our men’s counseling services at Medeor Hospital Abu Dhabi.